
Reconstruction with autologous tissues
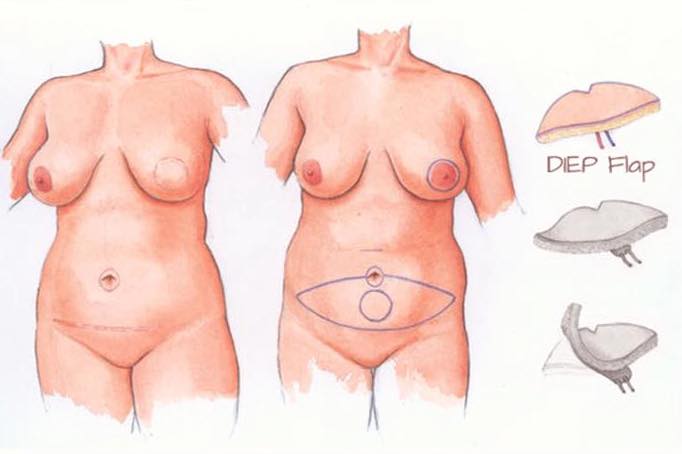
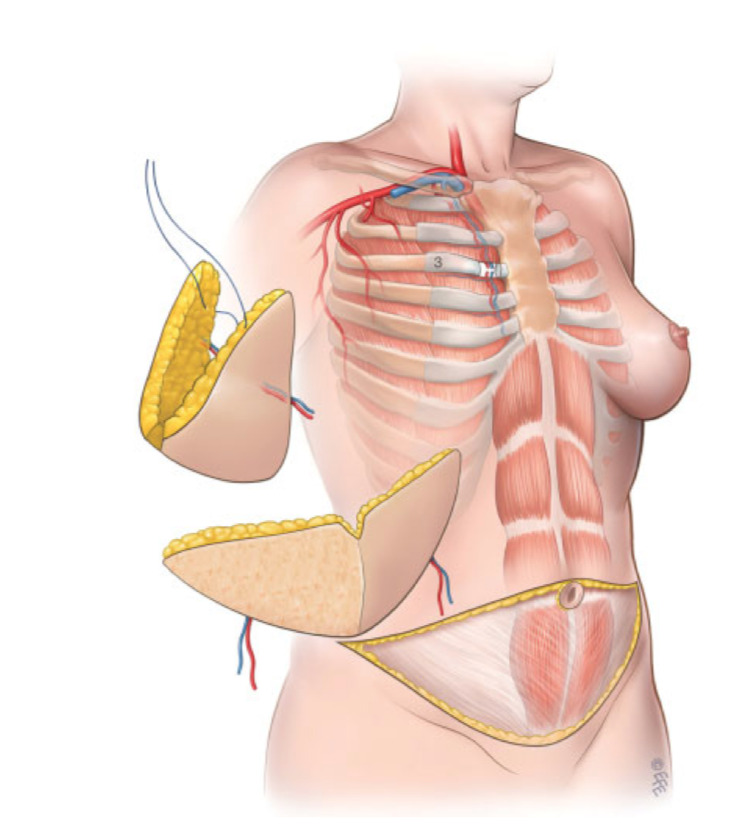
Breast reconstruction with autologous tissues involves the transposition of "flaps", or large amounts of tissue, usually composed of skin and subcutis, sometimes even muscle tissue. The flaps can be lifted and rotated towards the recipient area starting from adjacent donor areas, therefore with the persistence of a vascular peduncle originating from the collection area and connecting the recipient area with the donor area of origin (pedunculated island flaps), or they can be taken from other body regions distant from the donor area and then transferred to the recipient area by means of arteriovenous vascular anastomoses performed with microsurgery techniques (traditional free flaps / perforating free flaps).
More recently the "Lipofilling" technique has been introduced and is rapidly spreading.
The flaps were initially used in breast surgery only in selected cases characterized by large primary or secondary exeresis, therefore when the prosthetic reconstruction was not possible or had failed, in order to achieve simple coverage of the chest wall, but progressively the use of the flaps has assumed a predominant role in recreating the skin envelope and the volume of the breast without the use of prosthetic implants.
The main advantage offered by reconstruction with autologous tissues is that of reconstructing a "dynamic breast", that is subject to changes in shape and volume during movements and with changes in weight and age, following the modifications inevitably induced on the tissues by time and the force of gravity, similarly to what happens in the healthy breast. The result is a more natural and lasting result, with greater symmetry towards the contralateral breast, of which it reproduces the adipose-glandular structure well through the prevailing adipose component of the transferred flap, thus offering greater cosmetic value.
The surgeon is more able to reproduce a well-defined and symmetrical inframammary sulcus with the contralateral one. There is a lower incidence of complications compared to prosthetic reconstructions, still today burdened by frequent cases of capsular retraction and a non-negligible incidence of dehiscence of surgical wounds with implant exposure.
Autologous tissues do not interfere with radiotherapy, they benefit from lower care costs, despite the longer operating times, due to the intrinsic ability to reconstruct the breast in a single operation and without using biomaterials.
However, prosthetic implants, although characterized by the reconstruction of a “static” breast, still represent the most widely used reconstructive method in the world as they are technically less complex surgeries, which do not require an expert microsurgical team. In addition, they still represent the main reconstructive indication in patients of slender build, with small and rounded breasts and good conservation of thoracic tissues, in which good quality aesthetic results can be obtained even through prostheses.

Ricostruzione estetica microchirurgica mammaria
Affidati ad esperti nelle tecniche più avanzate in ricostruzione mammaria. Niente può darti un risultato migliore dei tuoi stessi tessuti!